Draw the open-chain structure of a 4-carbon deoxy sugar.

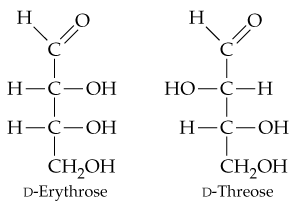
In Section 15.6, you saw that aldehydes react with reducing agents to yield primary alcohols (RCH=O → RCH2OH). The structures of two D-aldotetroses are shown. One of them can be reduced to yield a chiral product, but the other yields an achiral product. Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Aldehyde Reduction
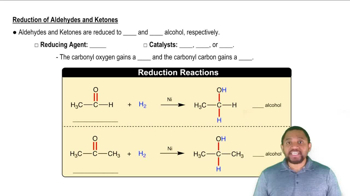
Chirality

Achirality

Name four important monosaccharides and tell where each occurs in nature.
Only three stereoisomers are possible for 2,3-dibromo-2, 3-dichlorobutane. Draw them, indicating which pair are enantiomers (optical isomers). Why does the other isomer not have an enantiomer?
Sucrose and D-glucose rotate plane-polarized light to the right; D-fructose rotates light to the left. When sucrose is hydrolyzed, the glucose–fructose mixture rotates light to the left.
b. Why do you think the mixture is called “invert sugar”?
In its open-chain form, D-mannose, an aldohexose found in orange peels, has the structure shown here. Coil mannose around and draw it in the cyclic hemiacetal ⍺ and β forms.
Treatment of D-glucose with a reducing agent yields sorbitol, a substance used as a sugar substitute by people with diabetes. Draw the structure of sorbitol.
