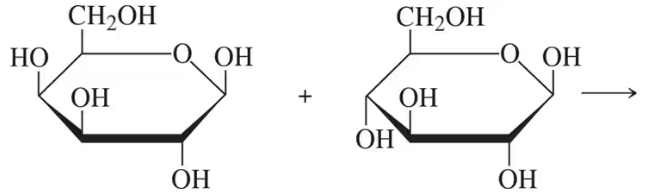
Consider the trisaccharide A, B, C shown in Problem 20.23.
a. Identify the hemiacetal and acetal linkages.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 1:44m
1:44mMaster Glycosidic Linkage Formation Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning