For the production of ammonia from its elements, ∆H = -22 kcal/mol(-19 kJ/mol).
b. How much energy (in kilocalories and kilojoules) is involved in the production of 0.700 mol of NH3?

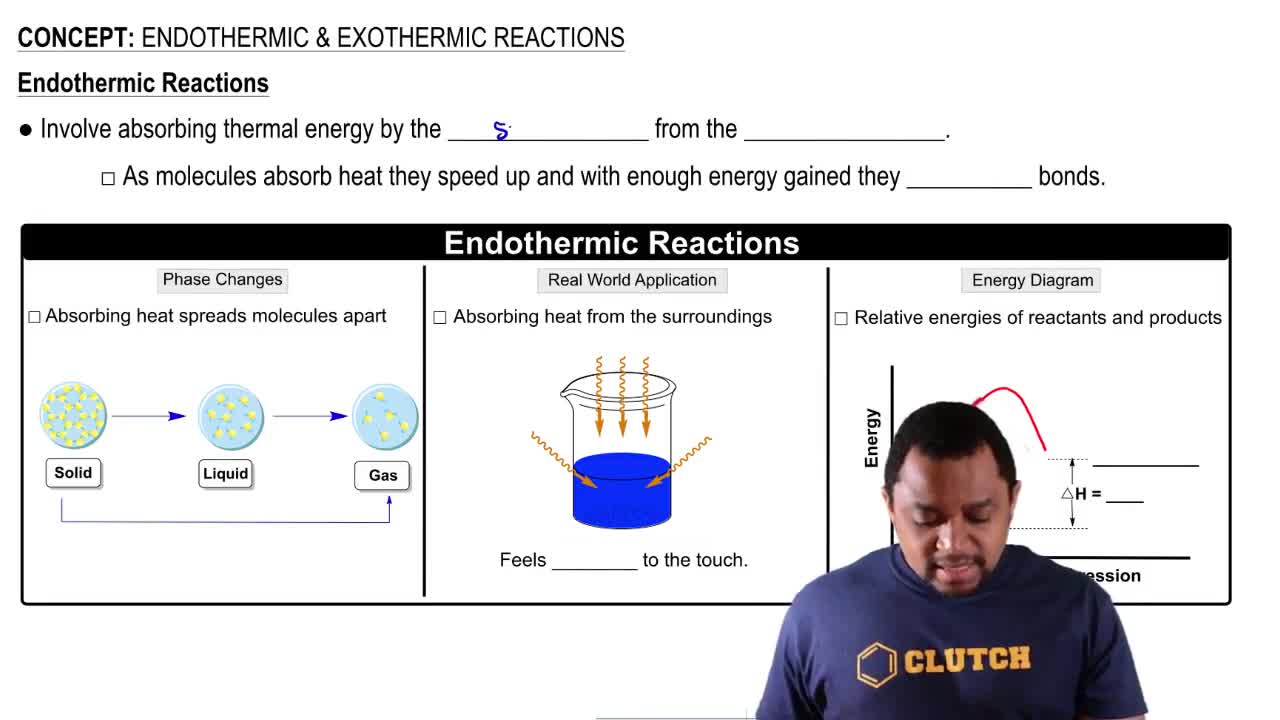
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


For the production of ammonia from its elements, ∆H = -22 kcal/mol(-19 kJ/mol).
b. How much energy (in kilocalories and kilojoules) is involved in the production of 0.700 mol of NH3?
Magnetite, an iron ore with formula Fe3O4, can be reduced by treatment with hydrogen to yield iron metal and water vapor.
a. Write the balanced equation.
Magnetite, an iron ore with formula Fe3O4, can be reduced by treatment with hydrogen to yield iron metal and water vapor.
d. This reaction has K = 2.3 × 10-18. Are the reactants or the products favored?
Ammonia reacts slowly in air to produce nitrogen monoxide and water vapor:
NH3(g) + O2(g) ⇌ NO(g) + H2O(g) + Heat
b. Write the equilibrium equation.
Methanol, CH3OH, is used as race car fuel.
c. How many kilojoules are released by burning 50.0 g of methanol?
Sketch an energy diagram for a system in which the forward reaction has Eact = +25 kcal/mol (+105 kJ/mol) and the reverse reaction has Eact = +35 kcal/mol (+146 kJ/mol).
a. Is the forward process endergonic or exergonic?