Textbook Question
Draw structures for molecules that fit the following descriptions:
(a) C3H6O containing an aldehyde functional group
1273
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

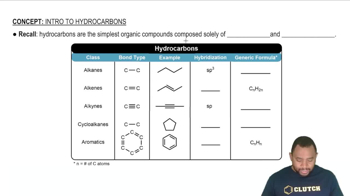

Draw structures for molecules that fit the following descriptions:
(a) C3H6O containing an aldehyde functional group
Draw structures for molecules that fit the following descriptions:
(c) C3H6O2 containing a carboxylic acid functional group
There are two branched-chain isomers with the formula C7H16, where the longest chain in the molecule is six carbons long. Draw them.
Draw the following three isomers of C5H12 as condensed structures:
a.
Draw the following three isomers of C5H12 as condensed structures:
b.