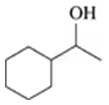
Write the balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of each of the following compounds:
b. 3-hexanol
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: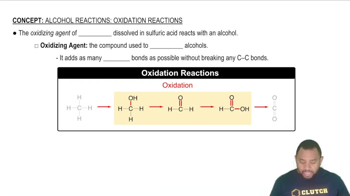



 1:49m
1:49mMaster Alcohol Reactions: Oxidation Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning