What are the molarity and the normality of a solution made by dissolving 25 g of citric acid (triprotic, C6H5O7H3) in enough water to make 800 mL of solution?

The dissociation of water into H3O+ and OH– ions depends on temperature. At 0 °C the [H3O+] = 3.38 x 10–8 M, at 25 °C the [H3O+] = 1.00 x 10–7 M, and at 50 °C the [H3O+] = 2.34 x 10–7 M.
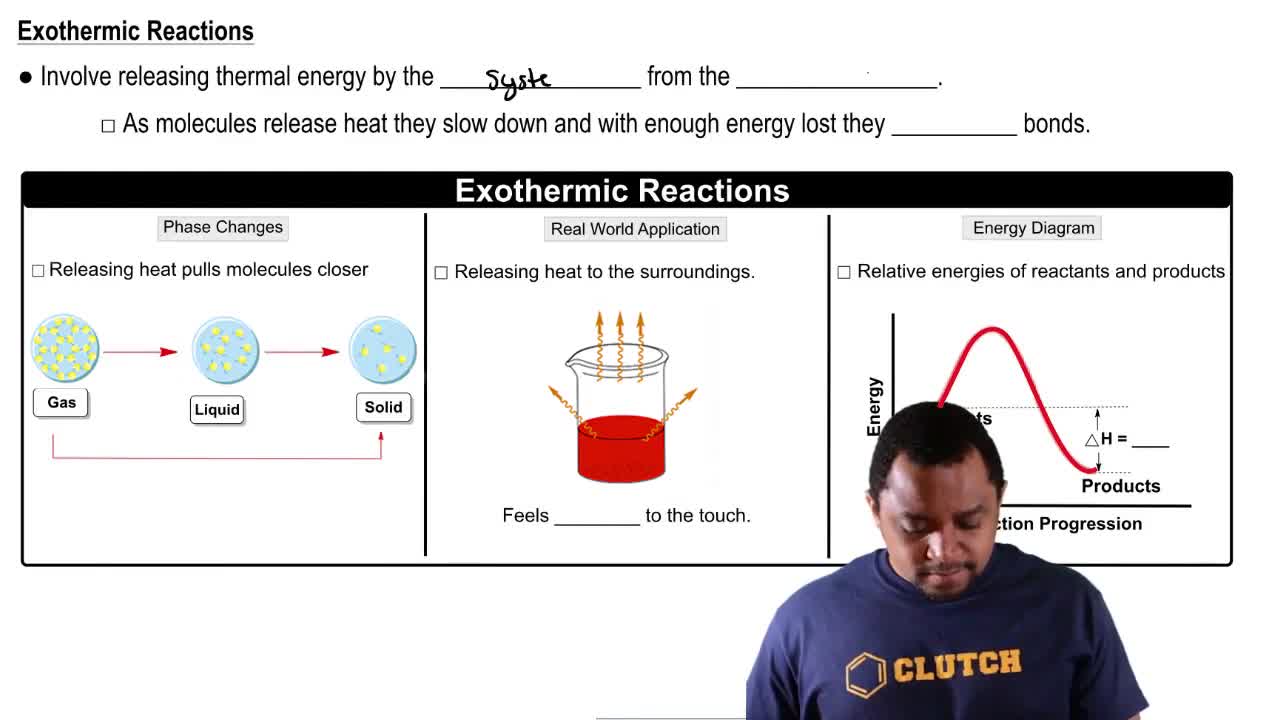
c. Is the dissociation of water endothermic or exothermic?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
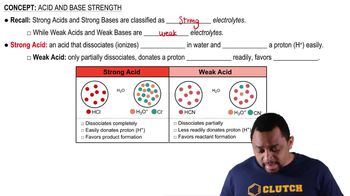
Key Concepts
Dissociation of Water
Endothermic vs. Exothermic Reactions
Temperature Dependence of Equilibrium

A solution is prepared by bubbling 15.0 L of HCl(g) at 25 °C and 1 atm into 250.0 mL of water.
a. Assuming all the HCl dissolves in the water, how many moles of HCl are in solution?
The dissociation of water into H3O+ and OH– ions depends on temperature. At 0 °C the [H3O+] = 3.38 x 10–8 M, at 25 °C the [H3O+] = 1.00 x 10–7 M, and at 50 °C the [H3O+] = 2.34 x 10–7 M.
b. What is the value of Kw at 0 °C and 50 °C?
One of the buffer systems used to control the pH of blood involves the equilibrium between H2PO4– and H2PO42–. The pKa for H2PO42– is 7.21.
a. Write the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for this buffer system.
Obtain a package of Alka-Seltzer, an antacid, from the local drug store:
b. Why does Alka-Seltzer foam and bubble when dissolved in water? Which ingredient is the antacid?
