Textbook Question
Reaction of Br2 and FeBr3 with phenol can lead to three possible substitution products. Show the structure of each and name them.
1712
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


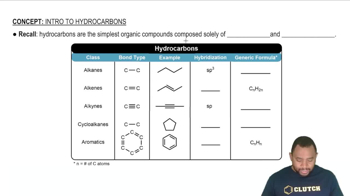
Reaction of Br2 and FeBr3 with phenol can lead to three possible substitution products. Show the structure of each and name them.
Draw the product from reaction of the following substances with (1) Br2 and FeBr3 and (2) SO3 and H2SO4 catalyst (red=O):
(a) <IMAGE>
(b) <IMAGE>
Alkynes undergo hydrogenation to give alkanes, just as alkenes do. Draw and name the products that would result from hydrogenation of the alkynes shown in Problem 13.25.
<IMAGE>
Draw an example of a saturated four carbon compound and an unsaturated four carbon compound.
What does the term 'aromatic' refer to when discussing organic molecules?
What is resonance and why is it important in aromatic compounds?