Textbook Question
Where within an atom are the three types of subatomic particles located?
1939
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

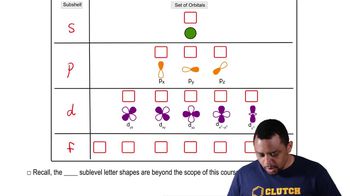

Where within an atom are the three types of subatomic particles located?
Why does the fourth period in the periodic table contain 18 elements?
Answer the following questions for the elements from cerium through lutetium:
a. Are they metals or nonmetals?
b. To what general class of elements do they belong?
c. What subshell is being filled by electrons in these elements?
How many subshells are there in the third shell? The fourth shell? The fifth shell?
Use arrows to show electron pairing in the valence p subshell of
a. Sulfur
b. Bromine
c. Silicon
What is the mass (in amu and in grams) of a single atom of Carbon-12?