Textbook Question
Which of the following molecules will produce the most ATP per mole?
a. glucose or stearic acid (C18)
176
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance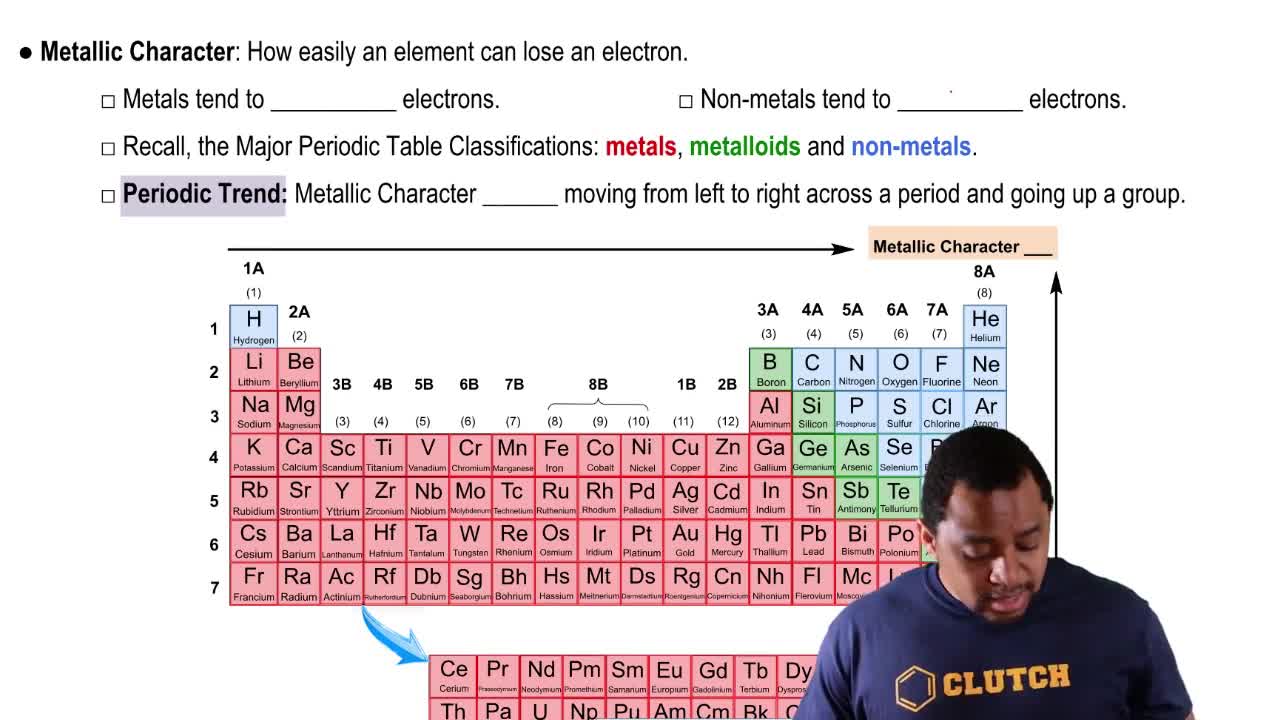
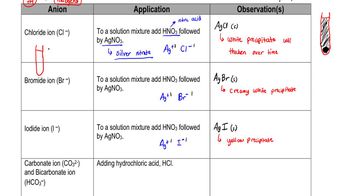
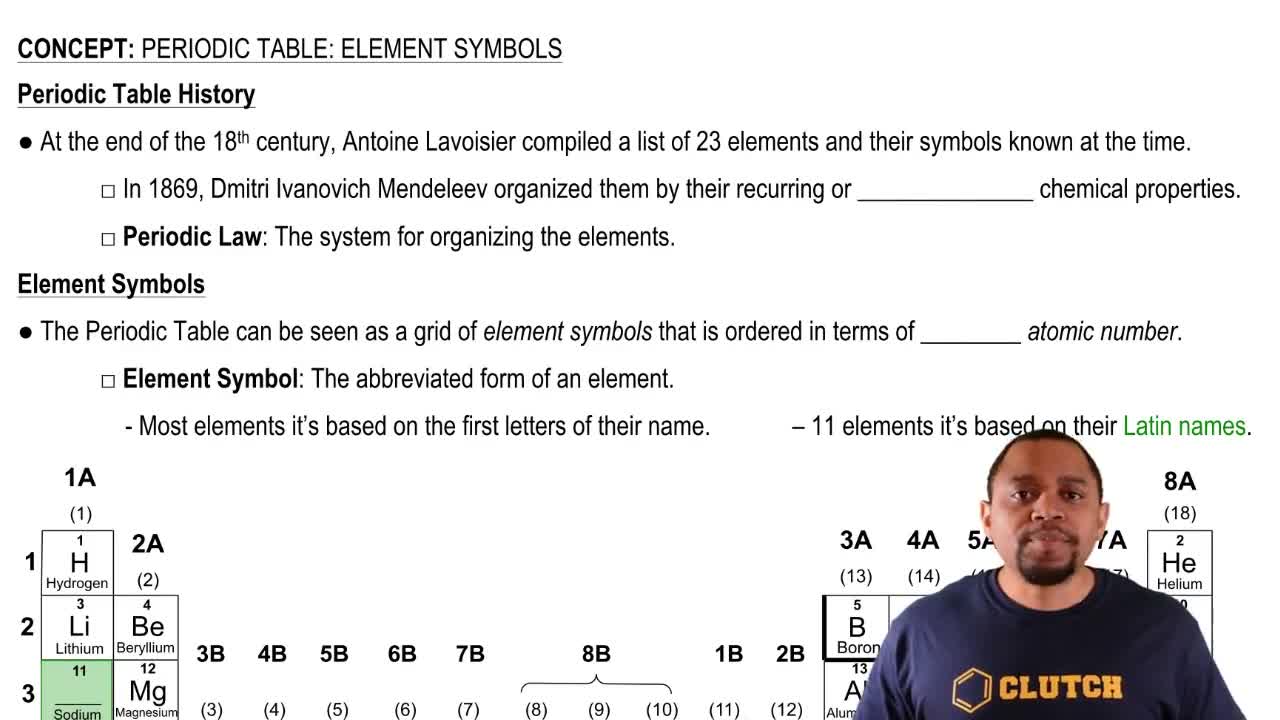
Which of the following molecules will produce the most ATP per mole?
a. glucose or stearic acid (C18)
Indicate if each of the following statements is true or false:
d. The proton and the electron have about the same mass.
Write the name and symbol of the element with the following atomic number:
h. 92