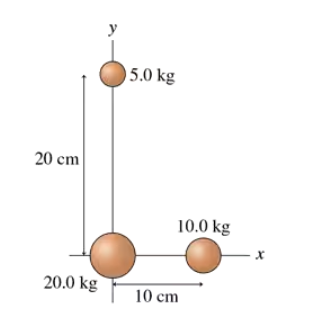
Textbook Question
What is the total gravitational potential energy of the three masses in FIGURE P13.36?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 4:52m
4:52mMaster Gravitational Potential Energy for Systems of Masses with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning