Textbook Question
A turntable of radius R₁ is turned by a circular rubber roller of radius R₂ in contact with it at their outer edges. What is the ratio of their angular velocities, ω₁/ω₂?
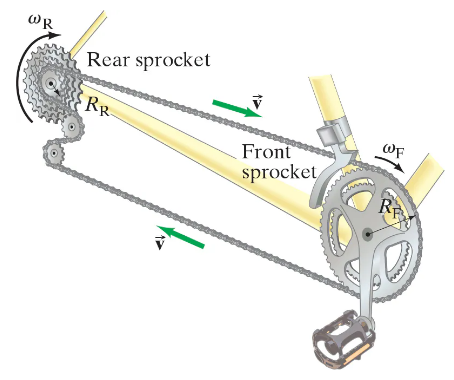
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 8:57m
8:57mMaster Intro to Connected Wheels with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning