Multiple Choice
There is a junction of three wires. flow into the junction along one path, and flow out along another path. How much charge flows in or out along the third path in ?
627
views
1
rank
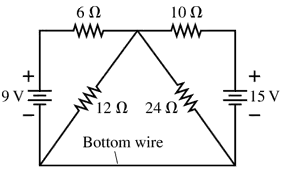
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 4:08m
4:08mMaster Kirchhoff's Junction Rule with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning