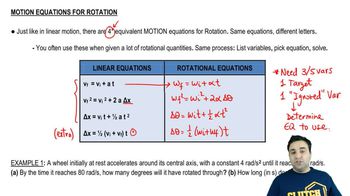
A tiny object spins with 5 rad/s around a circular path of radius 10 m. The object then accelerates at 3 rad/s2. Calculate its angular speed 8 s after starting to accelerate.
BONUS:Calculate its linear displacement in the 8 s.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 7:18m
7:18mMaster Equations of Rotational Motion with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning