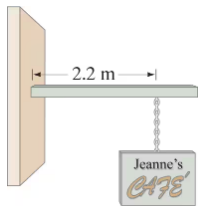
(II) You are on a pirate ship and being forced to walk the plank (Fig. 12–67). You are standing at the point marked C. The plank is nailed onto the deck at point A, and rests on the support 0.75 m away from A. The center of mass of the uniform plank is located at point B. Your mass is 65 kg and the mass of the plank is 45 kg. What is the minimum downward force the nails must exert on the plank to hold it in place?
<IMAGE>