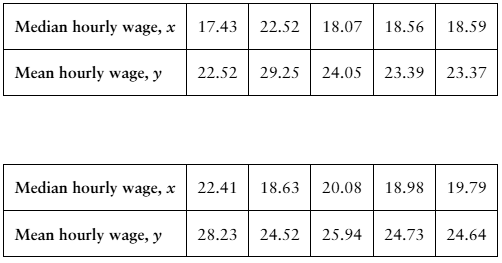
"In Exercises 7-10, use the value of the correlation coefficient r to calculate the coefficient of determination r^2. What does this tell you about the explained variation of the data about the regression line? about the unexplained variation?
7. r =0.465"