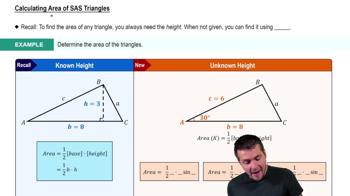
Textbook Question
In Exercises 41–42, find a to the nearest tenth.
515
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:27m
4:27mMaster Intro to Law of Sines with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning