Textbook Question
Solve each right triangle. When two sides are given, give angles in degrees and minutes. See Examples 1 and 2.
346
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: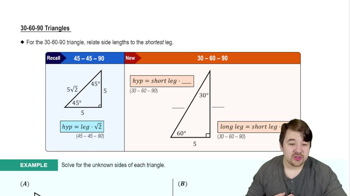



 4:18m
4:18mMaster Finding Missing Side Lengths with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning