The smallest unit capable of life by itself is:
a. The organ
b. The organelle
c. The tissue
d. The cell
e. The nucleus
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: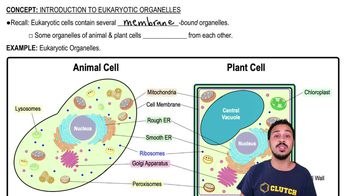

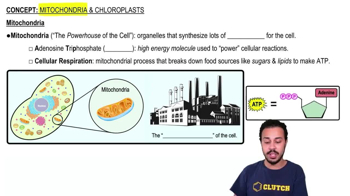

 5:54m
5:54mMaster Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning