Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures is found in animal cells but not in plant cells?
1895
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: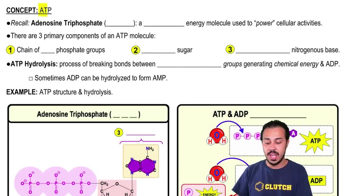

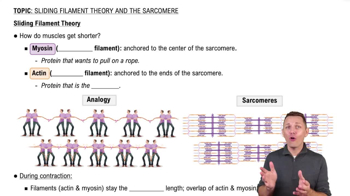

 6:05m
6:05mMaster Introduction to the Cytoskeleton with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning