Multiple Choice
Basal bodies are most closely associated with which of the following cell components?
2077
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

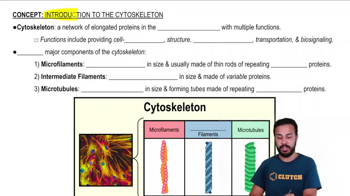

 6:05m
6:05mMaster Introduction to the Cytoskeleton with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning