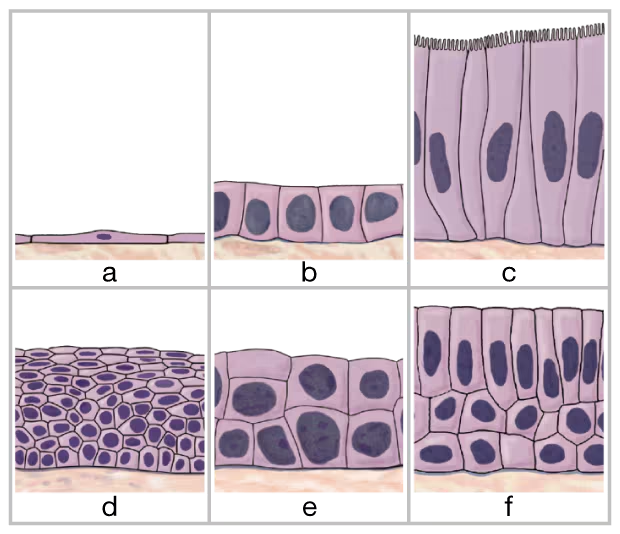
Which epithelium is 'built' to withstand friction?
a. Simple squamous
b. Stratified squamous
c. Simple cuboidal
d. Simple columnar
e. Pseudostratified
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 0:48m
0:48mMaster 5 Characteristics of Epithelia with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning