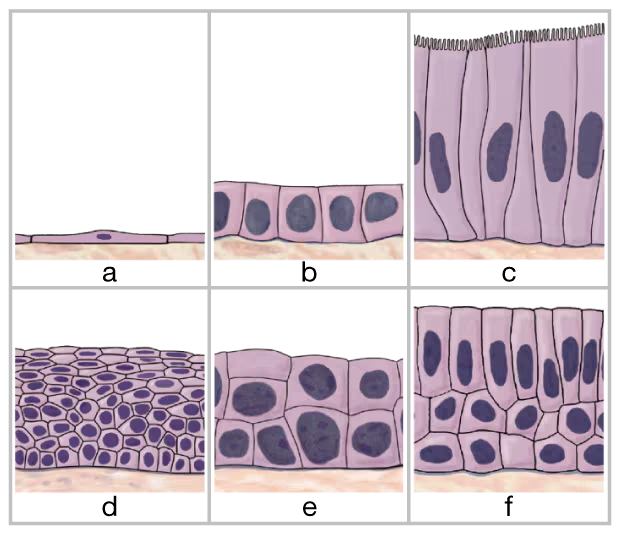
The most abundant connections between cells in the superficial layers of the skin are
(a) Connexons
(b) Gap junctions
(c) Desmosomes
(d) Tight junctions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 0:48m
0:48mMaster 5 Characteristics of Epithelia with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning