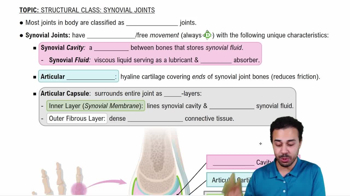
Match the types of joints to the descriptions that apply to them.
a. Fibrous joints
b. Cartilaginous joints
c. Synovial joints
3. Dense connective tissue fills the space between the bones
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 1:19m
1:19mMaster Introduction to Classification of Joints with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning