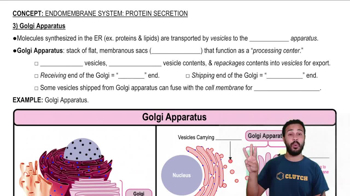
Textbook Question
What holds cellulose molecules together in bundles large enough to form fibers?a. the cell wallb. peptide bondsc. hydrogen bondsd. hydrophobic interactions
1710
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: