Multiple Choice
How do striated and smooth muscles differ in terms of structure and function?
243
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: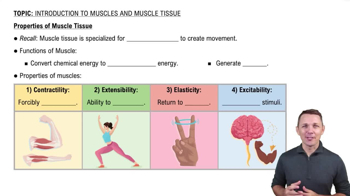


 0:36m
0:36mMaster 3 Types of Muscle Tissue with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning