Which of the following muscles attach to the hip bones?
a. Rectus abdominis
b. Rectus femoris
c. Vastus medialis
d. Vastus lateralis
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: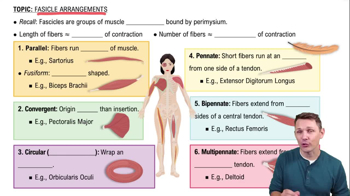


 5:39m
5:39mMaster Origin and Insertion with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning