Textbook Question
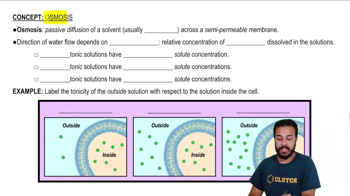
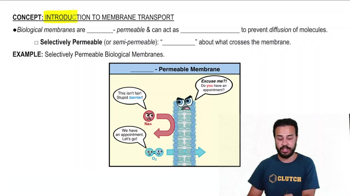
A plant cell placed in distilled water will ______________; an animal cell placed in distilled water will ______________.a. burst … burstb. become flaccid . . . shrivelc. become turgid . . . be normal in shaped. become turgid . . . burst
2591
views