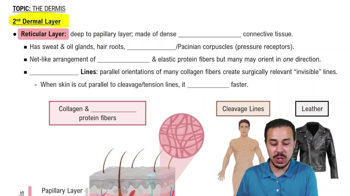
Textbook Question
What would be the sequence of the strand of DNA that is made from the following template: 5′-GATATCGAT-3′? (Your answer must be written 5'→3'.) How would the sequence be different if RNA were made from this DNA template?
1538
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: