More than one choice may apply.
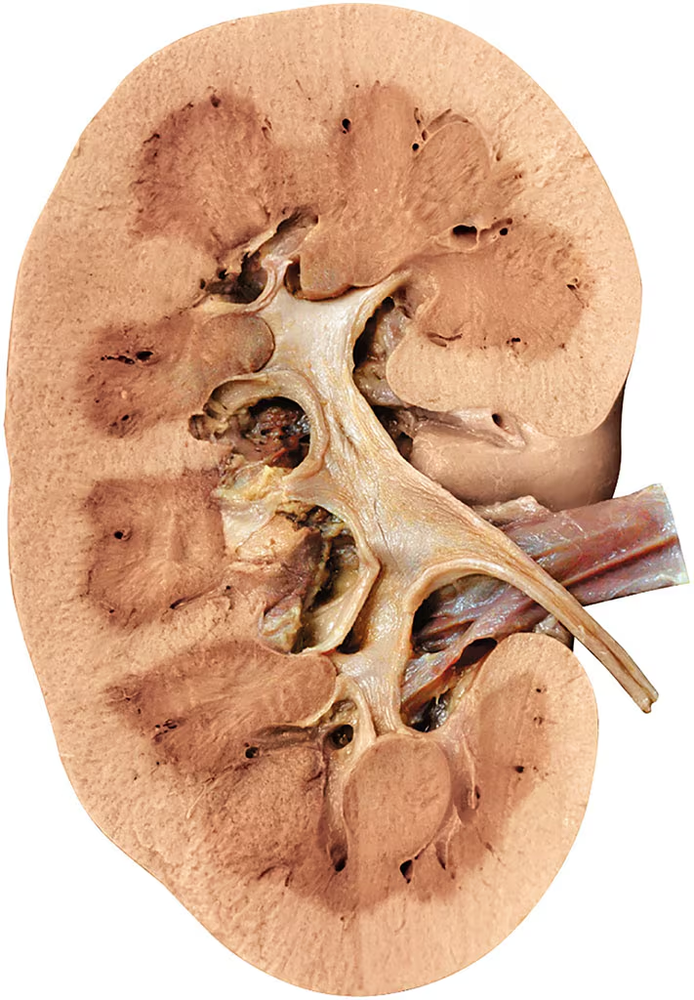
Match each letter from the figure with the correct blood vessel name.
Segmental arteries
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 3:44m
3:44mMaster External Anatomy with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning