Textbook Question
Describe the four structural components of the plasma membrane and the function of each.
55
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: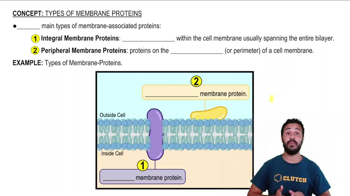



 6:49m
6:49mMaster Biological Membranes with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning