Multiple Choice
Which option below best describes a transporter that requires ATP to move molecules A and B out of the cell?
4290
views
64
rank
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
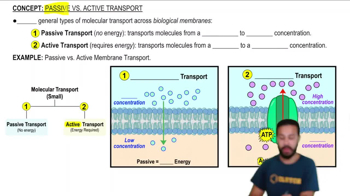


 5:05m
5:05mMaster Passive vs. Active Transport with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning