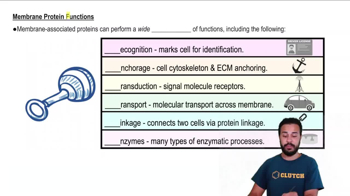
Textbook Question
What are the two types of secondary structures found in polypeptides, and what maintains them? What stabilizes the tertiary structure of a polypeptide?
1874
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: