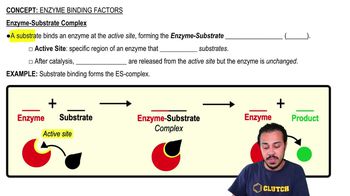
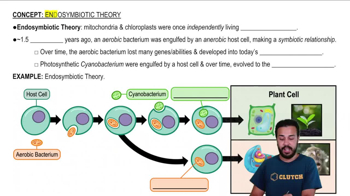
Textbook Question
Most proteins are soluble in the aqueous environment of a cell. Knowing that, where in the overall three-dimensional shape of a protein would you expect to find amino acids with hydrophobic R groups?
1856
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: