Multiple Choice
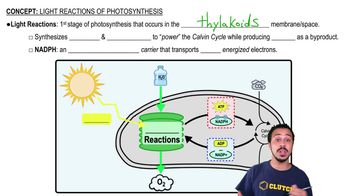
In green plants, what is the correct sequence of photosystems during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, and what does each photosystem primarily produce?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 3:16m
3:16mMaster Stages of Photosynthesis with a bite sized video explanation from Jason
Start learning