Multiple Choice
In prokaryotes, the rate of elongation during DNA replication is __________ the rate in eukaryotes.
1815
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

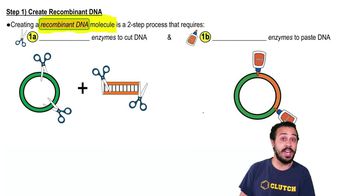

 3:37m
3:37mMaster Introduction to DNA Replication with a bite sized video explanation from Jason
Start learning