Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
DNA Polymerase Directionality
DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA in the 5' to 3' direction, which is crucial for understanding why Okazaki fragments are formed. On the lagging strand, DNA polymerase must work in short segments, creating Okazaki fragments, because it cannot synthesize in the 3' to 5' direction. This limitation necessitates the discontinuous synthesis of DNA on the lagging strand.
Recommended video:
Role of DNA Ligase
DNA ligase is an enzyme that joins DNA fragments together by forming phosphodiester bonds. It is used more frequently on the lagging strand during DNA replication because it is responsible for connecting the Okazaki fragments into a continuous strand. On the leading strand, DNA synthesis is continuous, requiring less frequent use of DNA ligase.
Recommended video:
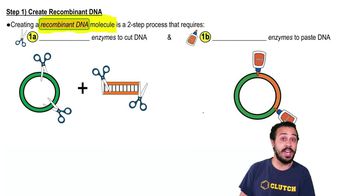
Step 1) Create Recombinant DNA
Function of Topoisomerase
Topoisomerase is an enzyme that helps relieve the tension in the DNA helix ahead of the replication fork by cutting, unwinding, and rejoining DNA strands. It is not directly involved in separating the two strands of DNA; this task is performed by helicase. Topoisomerase ensures that the DNA does not become overly coiled or tangled during replication.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 3:37m
3:37m