Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lac Operon Structure
The lac operon is a set of genes in E. coli that are involved in the metabolism of lactose. It consists of three structural genes (lacZ, lacY, and lacA) and regulatory elements, including a promoter and an operator. The operon is controlled by a repressor protein that binds to the operator region, preventing transcription when lactose is absent.
Recommended video:
Repressor Protein Function
The repressor protein is a key regulatory element in the lac operon. It binds to the operator region of the operon, blocking RNA polymerase from transcribing the downstream genes. When lactose is present, it binds to the repressor, causing a conformational change that prevents the repressor from binding to the operator, thus allowing transcription to occur.
Recommended video:
Membrane Protein Functions
Inducer Molecules
Inducers are molecules that trigger the expression of genes by inactivating repressors. In the case of the lac operon, allolactose, a derivative of lactose, acts as the inducer. When allolactose binds to the repressor, it alters the repressor's shape, preventing it from binding to the operator, which leads to the transcription of the lac genes necessary for lactose metabolism.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: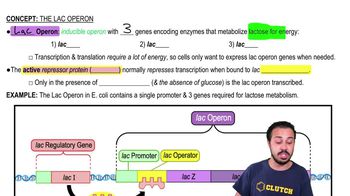



 0:53m
0:53m