Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lac Operon
The lac operon is a set of genes in E. coli that are involved in the metabolism of lactose. It includes structural genes, a promoter, an operator, and a repressor. The operon is a classic example of gene regulation, where the presence or absence of lactose influences the transcription of these genes.
Recommended video:
Repressor Protein
The repressor protein in the lac operon binds to the operator region to inhibit transcription. When lactose is absent, the repressor binds to the operator, preventing RNA polymerase from transcribing the genes. When lactose is present, it binds to the repressor, causing a conformational change that releases the operator, allowing transcription.
Recommended video:
Inducer
An inducer is a molecule that initiates gene expression. In the lac operon, allolactose acts as an inducer by binding to the repressor protein, altering its shape, and preventing it from binding to the operator. This allows RNA polymerase to access the promoter and transcribe the genes necessary for lactose metabolism.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: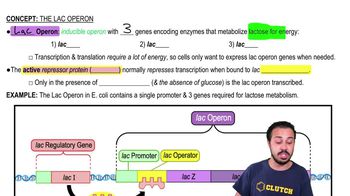



 0:53m
0:53m