A human's internal organs are protected mainly by the
a. Hydrostatic skeleton.
b. Axial skeleton.
c. Exoskeleton.
d. Appendicular skeleton.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: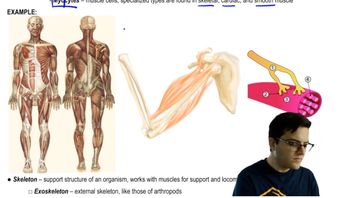



 2:08m
2:08mMaster Muscle System and Skeleton with a bite sized video explanation from Jason
Start learning