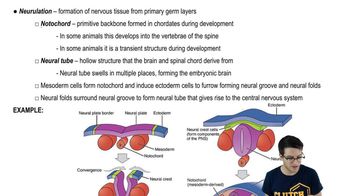
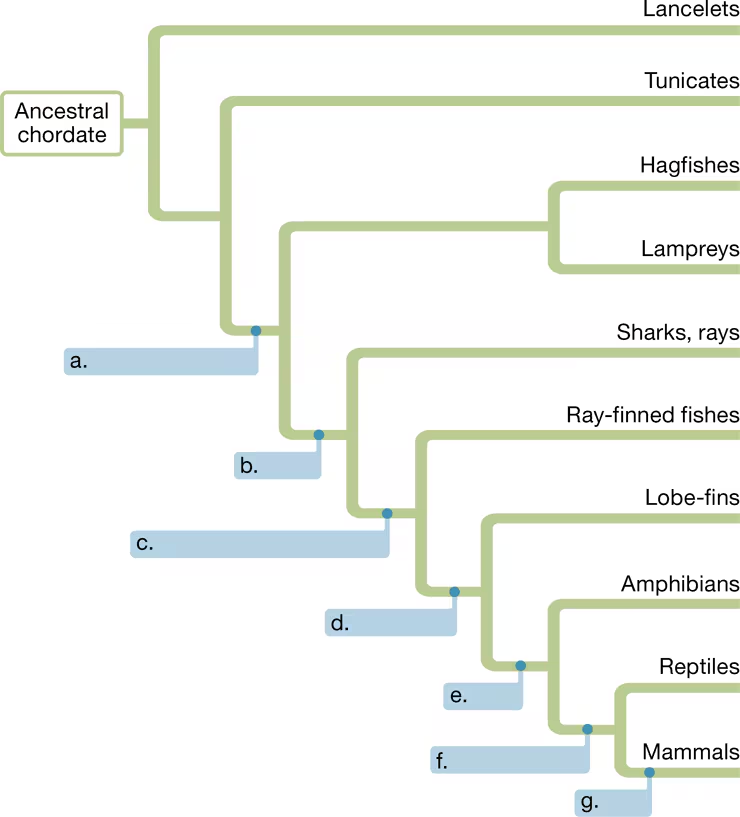
Vertebrates and tunicates share
a. Jaws adapted for feeding
b. A high degree of cephalization
c. An endoskeleton that includes a skull
d. A notochord and a dorsal, hollow nerve cord
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: