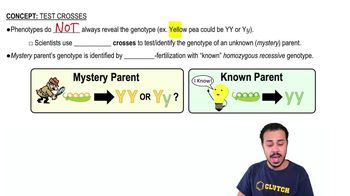
What do steroid and peptide hormones typically have in common?
a. Their solubility in cell membranes
b. Their requirement for travel through the bloodstream
c. The location of their receptors
d. Their reliance on signal transduction in the cell

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: