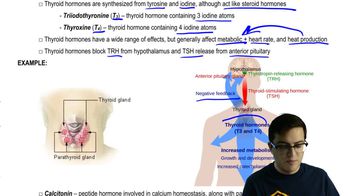
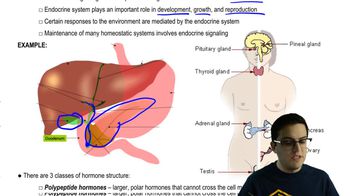
Which of the following is the most likely explanation for hypothyroidism in a patient whose iodine level is normal?
a. Greater production of T3 than of T4
b. Hyposecretion of TSH
c. Hypersecretion of MSH
d. A decrease in the thyroid secretion of calcitonin