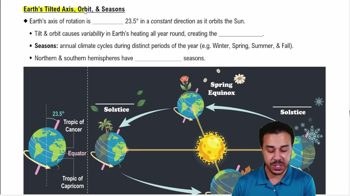
You have seen that Earth's terrestrial biomes reflect regional variations in climate. But what determines these climatic variations? Interpret the following diagrams in reference to how each represents effects on global patterns of temperature, rainfall, and winds.
a. Solar radiation and latitude
b. Earth's orbit around the sun
c. Global patterns of air circulation and rainfall