Textbook Question
In photosynthesis, _________ is oxidized and _________ is reduced.
a. Water . . . Oxygen
b. Carbon dioxide . . . Water
c. Water . . . Carbon dioxide
d. Glucose . . . Carbon dioxide
1437
views

 Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition
Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition Ch. 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food
Ch. 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food Problem 1
Problem 1 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


In photosynthesis, _________ is oxidized and _________ is reduced.
a. Water . . . Oxygen
b. Carbon dioxide . . . Water
c. Water . . . Carbon dioxide
d. Glucose . . . Carbon dioxide
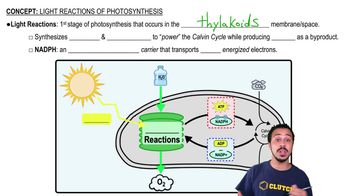
Which of the following are produced by reactions that take place in the thylakoids and consumed by reactions in the stroma?
a. CO₂ and H₂O
b. ATP and NADPH
c. ATP, NADPH, and CO₂
d. ATP, NADPH, and O₂
When light strikes chlorophyll molecules in the reaction-center complex, they lose electrons, which are ultimately replaced by
a. Splitting water
b. Oxidizing NADPH
c. The primary electron acceptor
d. The electron transport chain