Compare and describe the roles of CO₂ and H₂O in cellular respiration and photosynthesis.

 Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition
Taylor, Simon, Dickey, Hogan 10th Edition Ch. 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food
Ch. 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food Problem 14
Problem 14The following diagram compares the chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Identify the components that are shared by both organelles and indicate which side of the membrane has the higher H+ concentration. Then label on the right the locations within the chloroplast.
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Chemiosmosis
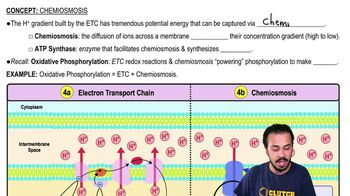
Proton Gradient

Organellar Structures

Continue your comparison of electron transport and chemiosmosis in mitochondria and chloroplasts. In each case:
a. Where do the electrons come from?
b. How do the electrons get their high potential energy?
c. What picks up the electrons at the end of the chain?
d. How is the energy released as electrons are transferred down the electron transport chain used?
Most scientific experts agree that climate change is already occurring and has potentially catastrophic consequences for all of life on Earth. The Paris Agreement of 2015 represented a global consensus on the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, in 2017 the United States announced its intention to withdraw from the Agreement in 2020. Go online to research and summarize the main agreements reached in this historic global climate accord and the U.S. government's reasons for withdrawing. What roles do you think scientists, politicians, and citizens will need to play to cut emissions and limit global warming?