Textbook Question
Solve each equation using the square root property. (x - 4)2 = -5
635
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
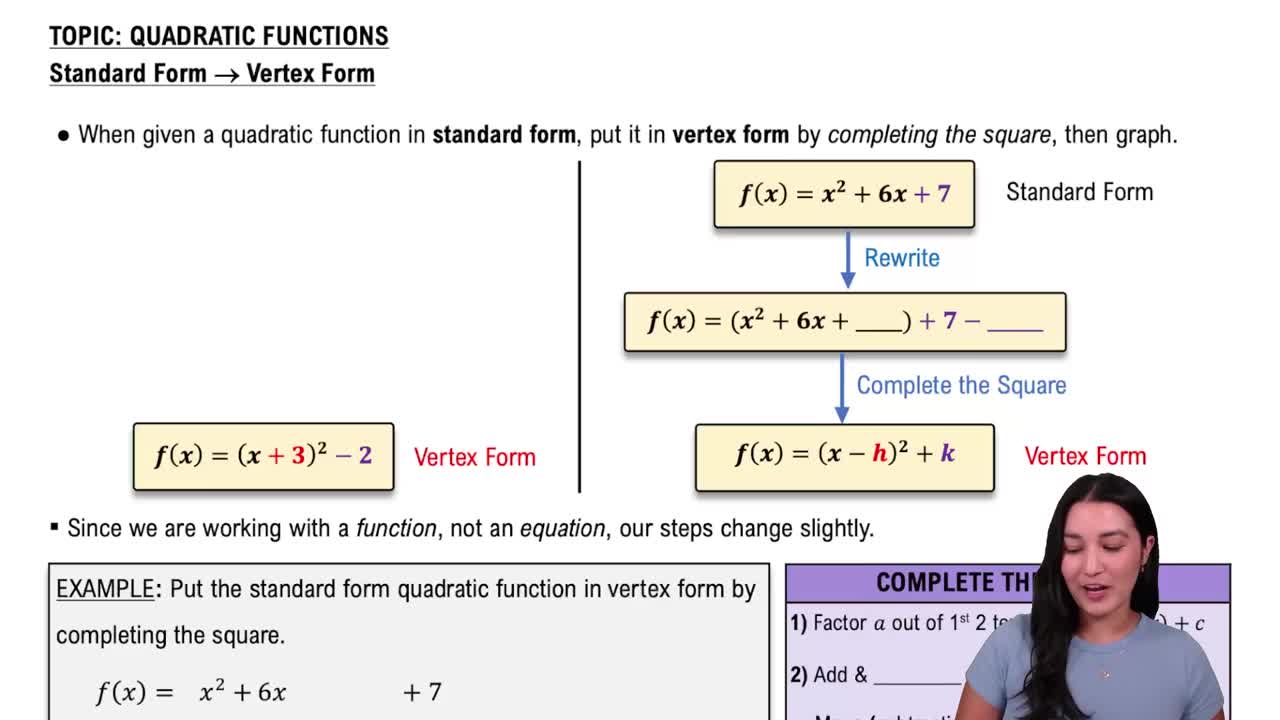
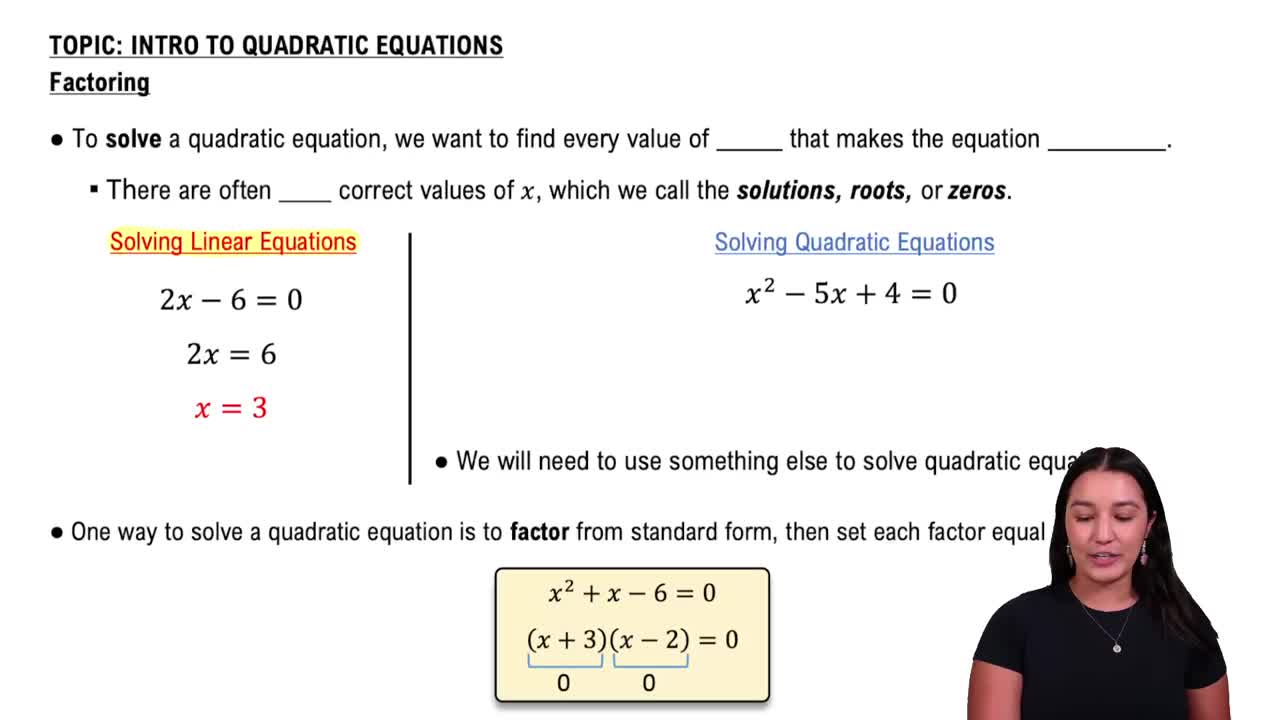

 6:12m
6:12mMaster Solving Quadratic Equations by the Square Root Property with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning