 Back
BackProblem 68a
Bupropion, marketed as Wellbutrin, is a heavily prescribed medication used in the treatment of depression. Complete the following electron-dot structure for Bupropion by adding lone pairs of electrons.
(a) How many s and how many p bonds are in the molecule?
- What is the hybridization of the B and N atoms in borazine, what are the values of the B¬N¬B and N¬B¬N bond angles, and what is the overall shape of the molecule?
Problem 70
- Benzyne, C6H4, is a highly energetic and reactive molecule. What hybridization do you expect for the two triply bonded carbon atoms? What are the 'theoretical' values for the C¬C‚C bond angles? Why do you suppose benzyne is so reactive?
Problem 71
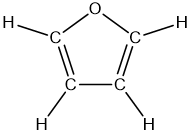
- Aspirin has the following connections among atoms. Complete the electron-dot structure for aspirin, tell how many s bonds and how many p bonds the molecule contains, and tell the hybridization of each carbon atom.
Problem 72

- The odor of cinnamon oil is due to cinnamaldehyde, C9H8O. What is the hybridization of each carbon atom in cinnamaldehyde? How many s and how many p bonds does cinnamaldehyde have?
Problem 75

- The following molecular model is a representation of caffeine. Identify the position(s) of multiple bonds in caffeine, and tell the hybridization of each carbon atom. 1Red = O, blue = N, gray = C, ivory = H.2
Problem 76

- What is the difference in spatial distribution between electrons in a bonding MO and electrons in an antibonding MO?
Problem 96
- For a given type of MO, use a s2s as an example, is the bonding or antibonding orbital higher in energy? Explain.
Problem 97
- Use the MO energy diagram in Figure 8.22b to describe the bonding in O2+, O2, and O2-. Which of the three is likely to be stable? What is the bond order of each? Which contain unpaired electrons?
Problem 98
- The C2 molecule can be represented by an MO diagram similar to that in Figure 8.22a. (b) To increase the bond order of C2, should you add or remove an electron?
Problem 100
- Look at the MO diagrams of corresponding neutral diatomic species in Figure 8.22, and predict whether each of the following ions is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Diagrams for Li2 and C2 are similar to N2; Cl2 is similar to F2. (c) F2-
Problem 102
- Calcium carbide, CaC2, reacts with water to produce acetylene, C2H2, and is sometimes used as a convenient source of that substance. Use the MO energy diagram in Figure 8.22a to describe the bonding in the carbide anion, C22-. What is its bond order?
Problem 105
Problem 106a
At high temperatures, sulfur vapor is predominantly in the form of S2(g) molecules. (a) Assuming that the molecular orbitals for third-row diatomic molecules are analogous to those for second-row molecules, construct an MO diagram for the valence orbitals of S2(g).
Problem 106d
At high temperatures, sulfur vapor is predominantly in the form of S2(g) molecules. (d) When two electrons are added to S2, the disulfide ion S22- is formed. Is the bond length in S22- likely to be shorter or longer than the bond length in S2? Explain.
Problem 107a
Carbon monoxide is produced by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. (a) Give the electron configuration for the valence molecular orbitals of CO. The orbitals have the same energy order as those of the N2 molecule.
Problem 107b
Carbon monoxide is produced by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. (b) Do you expect CO to be paramagnetic or diamagnetic?
Problem 107c
Carbon monoxide is produced by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. (c) What is the bond order of CO? Does this match the bond order predicted by the electron-dot structure?
- Make a sketch showing the location and geometry of the p orbitals in the nitrite ion, NO2-. Describe the bonding in this ion using a localized valence bond model for s bonding and a delocalized MO model for p bonding.
Problem 108
- In the cyanate ion, OCN-, carbon is the central atom. (d) Which hybrid orbitals are used by the C atom, and how many p bonds does the C atom form?
Problem 111
- The dichromate ion, Cr2O72-, has neither Cr¬Cr nor O¬O bonds. (b) How many outer-shell electrons does each Cr atom have in your electron-dot structure? What is the likely geometry around the Cr atoms?
Problem 113
Problem 115a
Cyclooctatetraene dianion, C8H82-, is an organic ion with the structure shown. Considering only the p bonds and not the s bonds, cyclooctatetraene dianion can be described by the following energy diagrams of its p molecular orbitals:
(a) What is the hybridization of the 8 carbon atoms?
Problem 115b
Cyclooctatetraene dianion, C8H82-, is an organic ion with the structure shown. Considering only the p bonds and not the s bonds, cyclooctatetraene dianion can be described by the following energy diagrams of its p molecular orbitals:
(b) Three of the p molecular orbitals are bonding, three are antibonding, and two are nonbonding, meaning that they have the same energy level as isolated p orbitals. Which is which?
Problem 115c
Cyclooctatetraene dianion, C8H82-, is an organic ion with the structure shown. Considering only the p bonds and not the s bonds, cyclooctatetraene dianion can be described by the following energy diagrams of its p molecular orbitals:
(c) Complete the MO energy diagram by assigning the appropriate numbers of p electrons to the various molecular orbitals, indicating the electrons using up/down arrows 1c T2.
- The water molecule has similar bond vibrations to carbon dioxide. Decide whether the symmetric, asymmetric, and bending vibrations in water will result in the absorption of IR radiation.
Problem 125
- Bond vibrations for the symmetric and asymmetric stretch in methane are illustrated below. Decide whether each vibration will result in the absorption of IR radiation. Arrows indicate the movement of atoms during the vibration.
Problem 126

- Values of Ea = 6.3 kJ>mol and A = 6.0 * 108>1M # s2 have been measured for the bimolecular reaction: NO1g2 + F21g2S NOF1g2 + F1g2 (b) The product of the reaction is nitrosyl fluoride. Its formula is usually written as NOF, but its structure is actually ONF. Is the ONF molecule linear or bent?
Problem 137
- (b) When xenon absorbs 801 kJ/mol of energy, it is excited into a higher-energy state in which the outermost elec-tron has been promoted to the next available subshell. Write the electron configuration for this excited xenon.
Problem 139
- The equilibrium constant Kc for the gas-phase thermal decom-position of cyclopropane to propene is 1.0 * 105 at 500 K:
Problem 153
(e) Why is cyclopropane so reactive? (Hint: Consider the hybrid orbitals used by the C atoms.)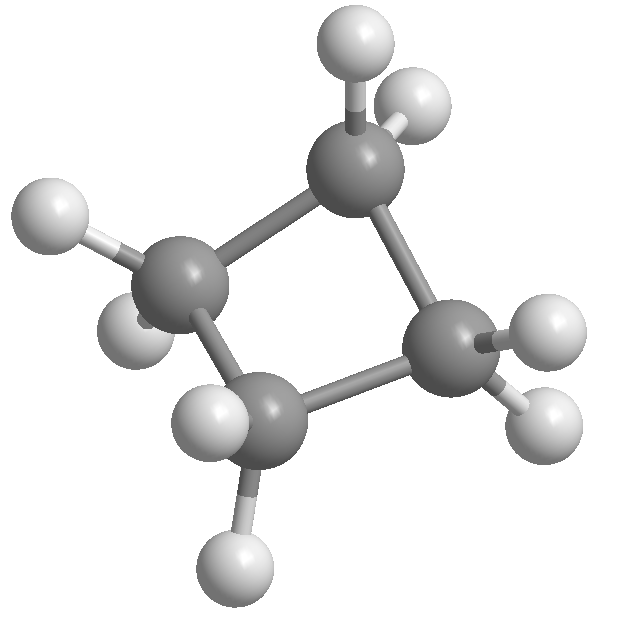
- Reaction of gaseous fluorine with compound X yields a sin- gle product Y, whose mass percent composition is 61.7% F and 38.3% Cl. (b) Draw an electron-dot structure for Y, and predict the geometry around the central atom.
Problem 155
