In each reaction, identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid, the Brønsted–Lowry base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate base. a. H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + HCO3–(aq) c. HNO3(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + NO3–(aq)
Ch.17 - Acids and Bases

Chapter 17, Problem 35d
In each reaction, identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid, the Brønsted–Lowry base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate base. d. C5H5N(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ C5H5NH+(aq) + OH–(aq)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid and base in the reactants: The Brønsted–Lowry acid is the species that donates a proton (H+), and the Brønsted–Lowry base is the species that accepts a proton.
In the given reaction, water (H2O) donates a proton to C5H5N, making H2O the Brønsted–Lowry acid.
C5H5N accepts a proton from H2O, making C5H5N the Brønsted–Lowry base.
Identify the conjugate acid and conjugate base in the products: The conjugate acid is the species formed when the base gains a proton, and the conjugate base is the species formed when the acid loses a proton.
C5H5NH+ is the conjugate acid formed from C5H5N, and OH- is the conjugate base formed from H2O.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Brønsted–Lowry Acid-Base Theory
The Brønsted–Lowry theory defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. In this framework, an acid-base reaction involves the transfer of protons (H+) from the acid to the base. This theory expands the understanding of acid-base reactions beyond just the presence of hydroxide ions, allowing for a broader range of reactions to be classified.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory
Conjugate Acid and Base
In the context of Brønsted–Lowry theory, a conjugate acid is formed when a base accepts a proton, while a conjugate base is what remains after an acid donates a proton. This relationship is crucial for understanding the equilibrium of acid-base reactions, as it illustrates how substances can act as both acids and bases depending on the reaction context.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Identifying Species in Reactions
To analyze acid-base reactions, it is essential to identify the reactants and products correctly. In the given reaction, C5H5N acts as a base by accepting a proton from water (acting as an acid), resulting in the formation of C5H5NH+ (the conjugate acid) and OH- (the conjugate base). This identification is key to understanding the roles of each species in the reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course
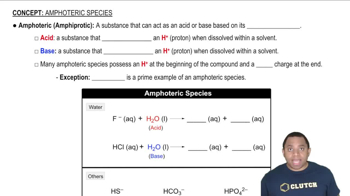
Amphoteric Species
Related Practice
Textbook Question
339
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
In each reaction, identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid, the Brønsted–Lowry base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate base. b. NH3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ NH4+(aq) + OH–(aq)
917
views
Textbook Question
In each reaction, identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid, the Brønsted–Lowry base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate base. b. CH3NH2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ CH3NH3+(aq) + OH–(aq)
459
views
Textbook Question
In each reaction, identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid, the Brønsted–Lowry base, the conjugate acid, and the conjugate base. c. CO32–(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCO3–(aq) + OH–(aq)
1097
views
Textbook Question
Write the formula for the conjugate base of each acid. a. HCl
1394
views
