In terms of the polycistronic composition of mRNAs and the presence or absence of Shine–Dalgarno sequences, compare and contrast bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic mRNAs.
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
11. Translation
Translation
Problem 39k
Textbook Question
Answer the following questions about the accompanying diagram.
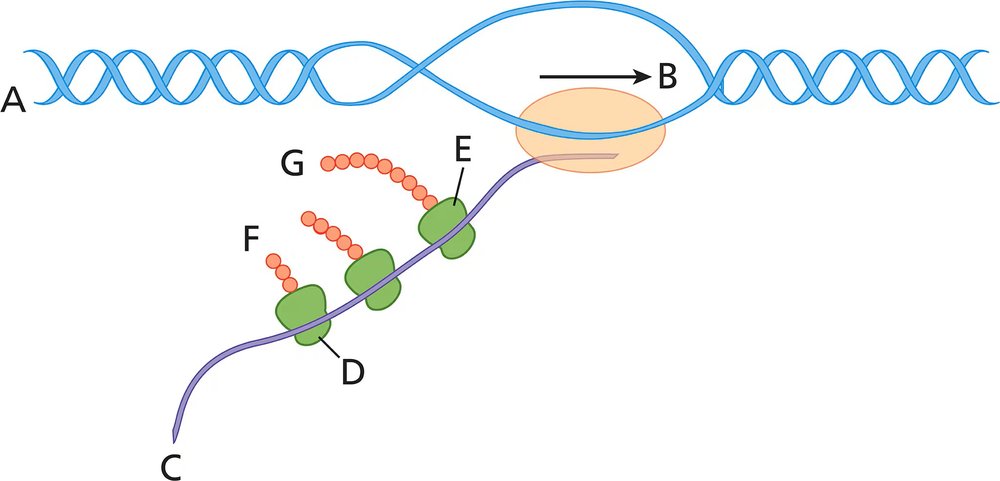
What process(es) are illustrated in the diagram?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Examine the diagram carefully. The image illustrates a process involving DNA (labeled A), mRNA (labeled C), ribosomes (labeled D), and polypeptide chains (labeled F and G). This suggests the diagram is depicting transcription and translation.
Identify the first part of the process. The DNA (A) is being transcribed into mRNA (C) by the enzyme RNA polymerase (labeled B). This is the transcription phase, where the genetic information in DNA is converted into a complementary RNA sequence.
Focus on the second part of the process. The mRNA (C) is interacting with ribosomes (D), which are facilitating the translation process. Translation is the synthesis of polypeptides (F and G) based on the sequence of codons in the mRNA.
Note the role of ribosomes (D). Ribosomes are responsible for reading the mRNA sequence and assembling amino acids into polypeptide chains (F and G) using tRNA molecules. This is a key step in protein synthesis.
Summarize the processes illustrated. The diagram shows two major processes in gene expression: transcription (DNA to mRNA) and translation (mRNA to polypeptide chains). These processes are essential for converting genetic information into functional proteins.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Translation
Translation is the process by which ribosomes synthesize proteins using messenger RNA (mRNA) as a template. During this process, the ribosome reads the sequence of codons in the mRNA, and transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring the corresponding amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. This is a crucial step in gene expression, converting genetic information into functional proteins.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Translation initiation
mRNA
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a type of RNA that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where proteins are synthesized. It is transcribed from the DNA template during transcription and contains codons that specify the sequence of amino acids in a protein. The structure of mRNA is linear and single-stranded, allowing it to be translated into proteins.
Recommended video:
Guided course

mRNA Processing
Ribosome
Ribosomes are complex molecular machines found within all living cells that facilitate the translation of mRNA into proteins. They consist of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins, forming two subunits that come together during protein synthesis. Ribosomes read the mRNA sequence and coordinate the assembly of amino acids into polypeptides, making them essential for cellular function and growth.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ribosome Structure

 7:58m
7:58mWatch next
Master Translation initiation with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
506
views
