Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Reciprocal Crosses
Reciprocal crosses involve mating two organisms in both possible combinations of their traits. For example, if one organism has trait A and the other has trait B, a reciprocal cross would involve crossing A with B and then B with A. This method helps to determine if the inheritance of traits is influenced by the sex of the parent, revealing potential differences in genetic contributions.
Recommended video:
Sex-Linked Inheritance
Sex-linked inheritance refers to genes located on sex chromosomes, which can lead to different expression patterns of traits based on the sex of the individual. For instance, if a trait is carried on the X chromosome, males (XY) and females (XX) may express the trait differently, leading to variations in the results of reciprocal crosses. Understanding this concept is crucial for interpreting the outcomes of genetic experiments.
Recommended video:
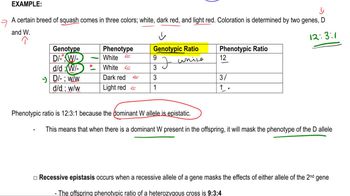
Genetic Epistasis
Genetic epistasis occurs when the expression of one gene is affected by one or more other genes. This interaction can lead to unexpected results in reciprocal crosses, as the presence of certain alleles may mask or modify the expression of others. To distinguish between epistasis and other genetic factors, specific crosses can be performed to analyze the phenotypic ratios and determine the underlying genetic interactions.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: